Earth and neutral are two different electrical concepts that are often confused. There is a common misunderstanding between the electrical concepts of earth and neutral. While they are related in some ways, they have distinct characteristics and serve different purposes in an electrical system. They have unique qualities and fulfill various functions in an electrical system, although they are related in some ways.
What is the difference between earth and neutral? First, let’s define each term. Earth, or ground, refers to an electrical connection to the ground or to a large conductive body that serves as a common reference point for electrical signals. This connection may be made using a rod or wire buried in the ground, or it may be made using the metal water pipes or reinforcing bars of a structure.
In the event of a fault or short circuit, grounding serves as a safe path for electrical current to flow, reducing the risk of electrical shock and equipment damage.
The chassis earth symbol shown above is a specially designed symbol that denotes a connection formed between an electrical equipment’s outside metal body and the earth for safety.
However, in electrical systems, the term “neutral” is used to describe the common return path or reference point for an electrical circuit. In a three-phase system, the neutral is the common point between the three phases, and in a single-phase system, it is the point between the live wire and the return wire. The neutral is not always connected to the earth, but it is frequently connected to the earth via a protective earth (PE) wire for added safety.
Now let’s understand the difference in real-life circuitry. We will take the three-phase star connection and delta system as examples to understand the neutral. Three phase star connection of a power generator consists of three windings. The end of each winding is connected to a common point, which is the neutral point of all windings.
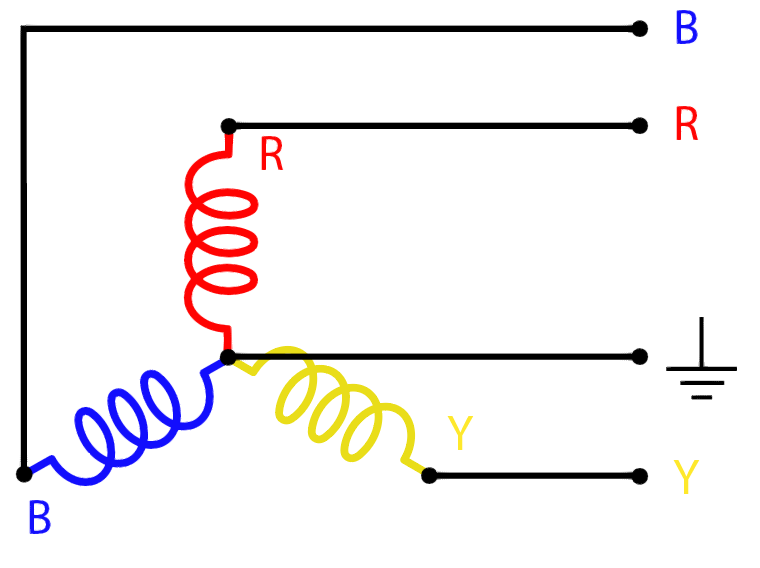
This type of neutral point is called system neutral, where each winding will show a voltage difference to the common point if the voltage is measured between one end of the coil and the neutral point of the common point. Now, if we try to measure voltage between the earth point and this neutral of the system, there will not be a reference to the ground unless there is any connection to the earth, but as soon as we connect that neutral to the earth, we will have a reference and a connection to the ground/earth and now we can use the earth as neutral.
The difference between earth and neutral is also their electrical potential. Since the earth is connected to a substantial conductive body with a relatively stable and constant potential, it is typically thought to have a potential of zero. The neutral, on the other hand, typically has a fluctuating potential depending on the circuit’s current. The neutral will have the same potential as the return wire in a single-phase system and the average potential of the three phases in a three-phase system.
Neutral could be at a different potential level or say high or low in voltage but the death will always have zero volt potential or electrically neutral. electrically neutral means no positive or negative charge.
In the delta connection, there is no common wire, so this system can’t be grounded, and earthing will not work in the case of the delta system.
Summary of differences between Earth and neutral
Purpose: The main difference between Earth and neutral is their purpose. Earth, or ground, refers to a connection to the ground or earth to set a zero-volt reference, which is basically used for providing safety. On the other hand, neutral is a term used in electrical systems to refer to the reference point or common return path for an electrical circuit.
Connection: Without neutral some systems won’t work. But most of the systems can work even if the earth is not available. Like in our household stuff, some use plugs with three pins for phase neutral and earth, but mobile phone chargers do not require an earth pin.
Electrical potential: A third difference between earth and neutral is their electrical potential. The earth is typically considered to have zero potential. On the other hand, neutral typically has a variable potential; depending on the circuitry, it may have a different potential than earth.
Safety: Earth is basically used for safety but can also be used as neutral.